Introduction
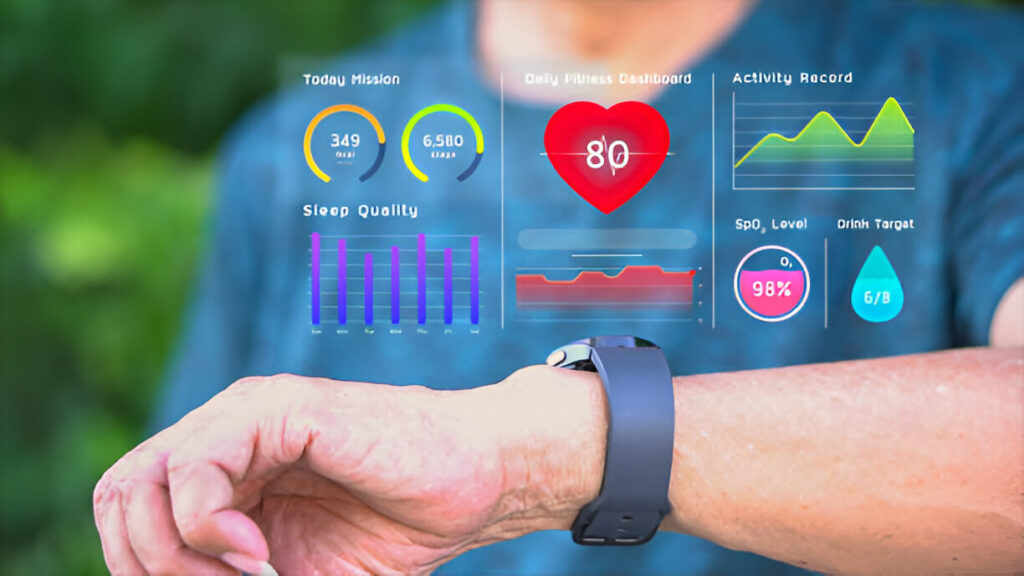
When wearable technology first entered the consumer market, fitness tracking was its primary focus—counting steps, monitoring heart rates, and logging workouts. Today, however, wearables have evolved into powerful, multi-functional devices that go far beyond health and fitness. From medical diagnostics and workplace safety to entertainment and augmented reality, wearable tech is reshaping how we live, work, and interact with the world.
1. Health Monitoring and Medical Applications
- Chronic Disease Management: Modern wearables can track glucose levels for diabetics, detect irregular heart rhythms, and monitor respiratory health.
- Preventive Healthcare: Continuous health monitoring allows for early detection of conditions such as sleep apnea or hypertension.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Doctors can receive real-time data from patients without the need for in-person visits, improving healthcare accessibility.
2. Workplace Productivity and Safety
- Industrial Safety Gear: Smart helmets and vests can detect fatigue, monitor exposure to hazardous substances, and alert workers to danger.
- Workplace Efficiency: AR-enabled smart glasses can display instructions directly in a worker’s field of vision, reducing downtime and errors.
- Location Tracking: GPS-enabled devices help monitor employee safety in high-risk industries like mining, construction, or offshore work.
3. Augmented and Virtual Reality Integration
- AR Glasses: Overlay digital information onto the real world for navigation, learning, or repair tasks.
- VR Headsets: Offer immersive training environments for pilots, surgeons, and engineers.
- Mixed Reality Collaboration: Enables remote teams to interact with 3D models and shared virtual spaces.
4. Fashion and Lifestyle Innovations
- Smart Clothing: Fabrics embedded with sensors can monitor posture, muscle activity, or hydration levels.
- Payment-Enabled Accessories: Smartwatches and even rings now allow contactless payments.
- Personal Safety Devices: Wearables with emergency alert features provide real-time GPS tracking in case of danger.
5. Entertainment and Gaming
- Haptic Feedback Wearables: Enhance gaming experiences with tactile sensations.
- Immersive Audio Devices: Smart earbuds can adapt sound profiles in real time for music, calls, and augmented reality experiences.
- Gesture-Controlled Devices: Allow users to interact with digital environments without a keyboard or controller.
6. Data Privacy and Security Considerations
While wearables offer numerous benefits, they also raise concerns:
- Sensitive Data Storage: Health and location data need strong encryption to prevent breaches.
- User Consent: Transparent data policies are essential to ensure ethical usage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Medical-grade wearables must meet strict standards for accuracy and safety.
7. The Future of Wearable Technology
- Smaller, Smarter, and Seamless: Devices will become more discreet, integrated into everyday accessories.
- AI-Driven Insights: Machine learning will provide more personalized and predictive data.
- Integration with IoT Ecosystems: Wearables will communicate more fluidly with smart homes, vehicles, and city infrastructure.
Conclusion
Wearable technology has moved far beyond simple fitness tracking to become a vital tool in healthcare, workplace safety, entertainment, and daily convenience. As innovation continues, wearables will increasingly blend into our lives—providing valuable insights, enhancing productivity, and improving quality of life. The challenge will be balancing these advancements with robust data privacy protections, ensuring that this powerful technology remains both beneficial and secure.